Introduction
Radiology has always been at the cutting edge of medical technology. From Wilhelm Röntgen’s discovery of X‑rays in 1895 to the development of CT, MRI, and PET scans, imaging has revolutionized diagnosis and treatment. Today, radiology is undergoing another transformation — powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
AI is no longer confined to research labs; it is being integrated into clinical workflows, assisting radiologists in detecting disease, predicting outcomes, and even guiding treatment. This article explores how AI is reshaping radiology, the evidence behind its use, and the challenges that remain.
The Rise of AI in Medical Imaging
AI in radiology primarily relies on deep learning, a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks to analyze complex data. These algorithms can be trained on millions of images to recognize patterns that may be invisible to the human eye.
- Image recognition: Detecting tumors, fractures, or hemorrhages.
- Segmentation: Outlining organs or lesions for precise measurement.
- Classification: Distinguishing between benign and malignant findings.
- Prediction: Estimating disease progression or treatment response.
(Reference: Esteva et al., Nature, 2017 — “Dermatologist‑level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks.”)
Clinical Applications
1. Cancer Detection
- AI systems have shown performance comparable to radiologists in detecting breast cancer on mammograms.
- In lung cancer screening, AI improves detection of small nodules on CT scans. (Reference: McKinney et al., Nature, 2020 — Google Health mammography AI study.)
2. Neurology
- AI can rapidly identify strokes on CT scans, enabling faster intervention.
- Algorithms detect microbleeds and subtle white matter changes linked to dementia. (Reference: Muehlematter et al., Radiology, 2021.)
3. Musculoskeletal Imaging
- AI assists in detecting fractures, particularly in emergency settings where speed is critical.
- Automated joint space analysis helps track osteoarthritis progression.
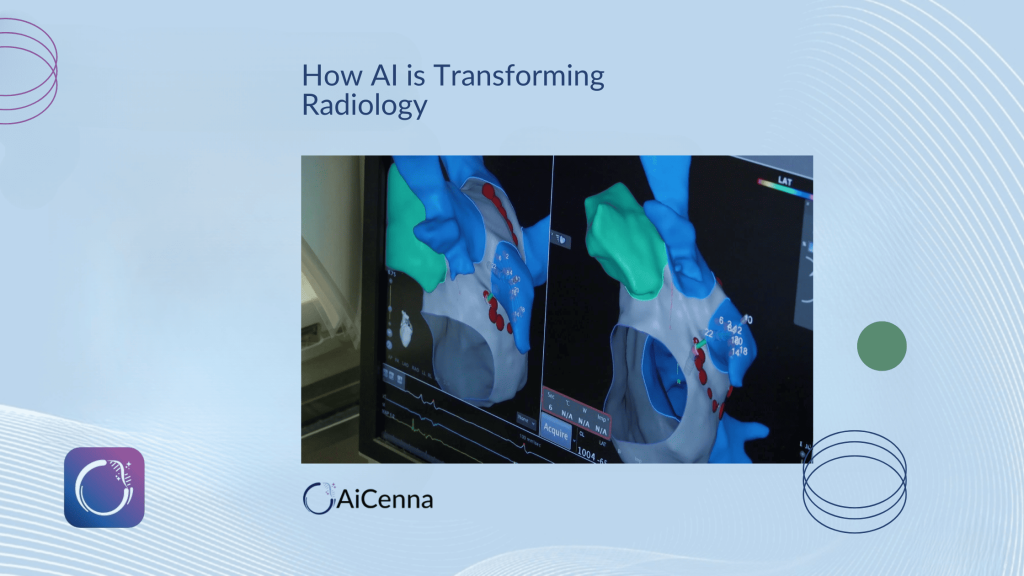
4. Cardiology
- AI enhances echocardiography by automating measurements of ejection fraction.
- Predictive models estimate risk of heart failure based on imaging and clinical data.
Beyond Detection: Predictive Insights
AI is moving radiology from descriptive to predictive and prescriptive medicine.
- Radiomics: Extracting quantitative features from images (texture, shape, intensity) to predict tumor behavior.
- Prognostic modeling: AI can forecast which patients are likely to respond to chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
- Population health: Large‑scale imaging data combined with AI can identify public health trends, such as early signs of osteoporosis in populations.
(Reference: Lambin et al., Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2017 — “Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images.”)
Benefits for Radiologists and Patients
- Efficiency: AI automates routine tasks, freeing radiologists to focus on complex cases.
- Accuracy: Reduces missed diagnoses, especially in high‑volume settings.
- Consistency: Minimizes variability between readers.
- Access: AI tools can extend expertise to underserved areas lacking radiologists.
Challenges and Limitations
1. Data Quality
- AI is only as good as the data it is trained on. Bias in datasets can lead to unequal performance across populations.
2. Interpretability
- Many AI models are “black boxes,” making it difficult to explain decisions. Clinicians need transparency to trust results.
3. Regulation
- The FDA and European regulators are developing frameworks for AI in medicine, but standards are still evolving.
4. Integration
- Embedding AI into existing workflows requires interoperability with hospital IT systems.
5. Ethical Concerns
- Patient privacy, informed consent, and liability in case of errors remain unresolved.
(Reference: Topol, E. “High‑performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence.” Nat Med, 2019.)
What Radiologists Say
Surveys show that most radiologists view AI not as a replacement but as a partner. The consensus is that AI will augment human expertise, handling repetitive tasks while radiologists focus on interpretation, communication, and patient care.
(Reference: European Society of Radiology, Insights into Imaging, 2019.)
The Future of AI in Radiology
- Real‑time decision support: AI integrated into scanners providing instant feedback.
- Multimodal integration: Combining imaging with genomics, pathology, and clinical data for holistic insights.
- Continuous learning systems: AI that updates itself as new data becomes available.
- Global equity: Cloud‑based AI tools could bring advanced diagnostics to low‑resource settings.
(Reference: Nature Medicine, 2021 — “Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: opportunities and challenges.”)
Conclusion
AI is transforming radiology from a discipline focused on detecting disease to one capable of predicting outcomes and guiding treatment. While challenges remain in data quality, regulation, and ethics, the trajectory is clear: AI will not replace radiologists but will empower them.
The radiology department of the future may look very different — not because humans are absent, but because they are working side by side with intelligent systems that extend their vision, speed, and precision.